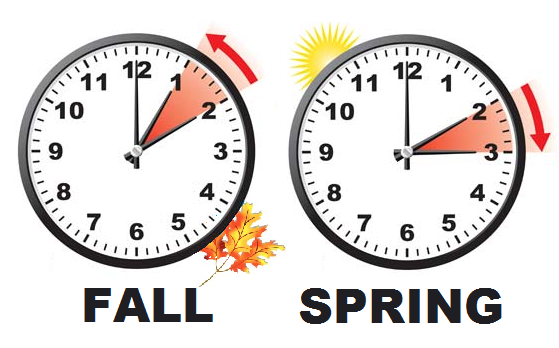
Last Sunday, March 10, most Americans set their clocks forward an hour, as daylight saving time begins, and most of the United States will "gain" an hour of daylight.
These spring and fall clock changes continue a long tradition started by Benjamin Franklin to conserve energy. Learn how this tradition works!
Historically, daylight saving time has begun in the summer months and ended for winter, though the dates have changed over time as the U.S. government has passed new statutes, according to the U.S. Naval Observatory (USNO).
Starting in 2007, DST begins in the United States on the second Sunday in March, when people move their clocks forward an hour at 2 a.m. local standard time (so at 2 a.m. on that day, the clocks will then read 3 a.m. local daylight time). Daylight saving time ends on the first Sunday in November, when clocks are moved back an hour at 2 a.m. local daylight time (so they will then read 1 a.m. local standard time).
How Did It Start?
Benjamin Franklin takes the honor (or the blame, depending on your view of the time changes) for coming up with the idea to reset clocks in the summer months as a way to conserve energy, by moving clocks forward, people could take advantage of the extra evening daylight rather than wasting energy on lighting.
At the time, Franklin was ambassador to Paris and so wrote a witty letter to the Journal of Paris in 1784, rejoicing over his "discovery" that the sun provides light as soon as it rises.

Why do we still have daylight saving time?
Fewer than 40% of the world's countries observe daylight saving time, according to timeanddate.com. However, those who do observe DST take advantage of the natural daylight in the evenings. That's because the days start to get longer as Earth moves from the winter season to spring and summer, with the longest day of the year on the summer solstice. During the summer, Earth, which revolves around its axis at an angle, is tilted directly toward the sun (at least its top half)
Regions farthest away from the equator and closer to the poles get the most benefit from the DST clock change, because there is a more dramatic change in sunlight throughout the seasons.
Research has also suggested that with more daylight in the evenings, there are fewer traffic accidents, as there are fewer cars on the road when it's dark outside. More daylight also could mean more outdoor exercise (or exercise at all) for full-time workers.

Fun Facts
- Pets notice the time change, as well. Since humans set the routines for their fluffy loved ones, dogs and cats living indoors and even cows are disrupted when, say, you bring their food an hour late or come to milk them later than usual, according to Alison Holdhus-Small, a research assistant at CSIRO Livestock Industries, an Australia-based research and development organization.
-The fact that the time changes at 2 a.m. at least in the U.S., may have to do with practicality. For instance, it's late enough that most people are home from outings and setting the clock back an hour won't switch the date to "yesterday." In addition, it's early enough not to affect early shift workers and early churchgoers, according to the WebExhibits, an online museum.
Want to learn more amazing facts?
Check more Smart Fridays articles!
Check the original article here: https://www.livescience.com/56048-daylight-saving-time-guide.html

