For the first time, TEKS include product specific standards for robotics arm, highlighting the importance for the students to take part in and understand Industry 4.0 is the current trend of automation and data exchange in manufacturing technologies that will shape their future. It provide hands-on Computer Science for students and brings coding to life.
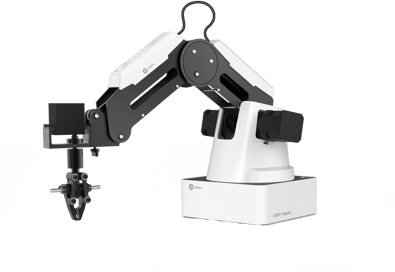
Dobot Magician integrates programming, mechanics, electronics, and automation. It’s a great STEAM teaching device that strengthens knowledge across multiple subjects, through a high precision and user-friendly UI. It also provides, enjoyable functions, and unlimited developing possibilities. Dobot Magician’s captivating and exploratory experience increases interest in science and technology.
The advantages of high precision (0.2mm) and switchable tool heads allow students to perform 3D printing, pick and place, write and draw, and more. Combining these different uses brings out even more fun, learning, and creativity through unlimited possibilities. Also, Dobot Magician is the first robotic arm that is 3D print accessible to schools and students.
The Dobot is a versatile platform that can be programmed using Blockly, Apple Swift Playgrounds, Python, C/C++, Arduino, Android Studio, Java, C#, Visual Basic and Dobot Studio. The hardware can be extended as well using standard ports that match Arduino, Raspberry Pi and many other off-the-shelf electronics
Dobot Magician is a truly cutting-edge robotic arm that is now available for your STEAM or CTE program. It's a highly cost- effective solution that empowers 21st century skills by unleashing students' creativity.
TEKS 2017-2018
§130.408.8 - The student develops an understanding of the characteristics and scope of manipulators, accumulators, and end effectors required for a robotic or automated system to function. The student is expected to:
§130.408.8 - (A) describe the relationship between robotic arm construction and robot stability;
§130.408.8- (B) describe the relationship between torque and gear ratio to weight of payload in a robotic arm operation;
§130.408.8- (C) demonstrate knowledge of linkages and gearing in end effectors used in a robotic arm system
§130.409.7 - (B) describe the term degrees of freedom and apply it to the design of joints used in robotic and automated systems;
§130.409.7 - (E) explain translational, rotational, and oscillatory motion in the design of robotic and automated systems;
§130.409.9 - The student develops an understanding of the characteristics and scope of manipulators, accumulators, and end effectors required for a robotic or automated system to function. The student is expected to:
§130.409.9 - (A) demonstrate knowledge of robotic or automated system arm construction;
§130.409.9- (B) demonstrate an understanding and apply the concepts of torque, gear ratio, stability, and weight of payload in a robotic automated system arm operation;
§130.409.9 - (C) demonstrate an understanding and apply the concepts of linkages and gearing in end effectors and their use in a robotic or an automated arm system.

RobotLAB creates a program that makes the CTE classroom engaging and relevant to the lives of students. Plus, classrooms can fulfill their educational standards by adapting it into a powerful, all-in-one tool for student learning.
If you are interested in learning more about Dobot Robotic Arm you can ask for a price quote request.
